Nuclear energy is widely used to produce electricity as it is cheap, efficient, and environmentally friendly. It does not require natural sources such as wind, water, or solar power. But it must be controlled and maintained properly. The slightest error can cause huge damage that will affect all living beings on earth. In 1986, April 26th, the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant’s reactor number 4 blasted releasing tons of radiation to the open air. Around 30 workers and firefighters who approached the site to put up the fire died within 4 months of radiation poisoning. It made about 2500 square kilometers of land on earth inhabitable for any living being for another 10,000 years.
How a Nuclear Power Plant works
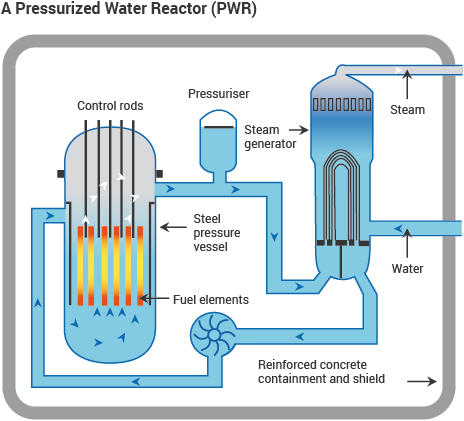
In the nuclear power plant, the electricity is produced by turning a turbine using high-pressure steam. Heat is produced by the fission of unstable atoms such as Uranium-235. These Uranium rods which are called reactor rods are kept cool by circulating water around them. This water does not evaporate as they maintain the pressure inside the container in which the reactors are placed. This heated water is then circulated through metal pipes dipped in water in a separate chamber and heats the water inside it to produce steam which turns the turbine. Reactivity or power of the reactor is controlled by raising or lowering control rods made of Boron or Cadmium which absorb neutrons and reduce the fission rate. Water must always circulate the core to cool it and this radiated water will not leave the reactor. This is the simple mechanism of the Nuclear power plant.
The nuclear reaction inside the reactor
When Uranium-235 absorbs a neutron, it turns into Uranium 236 which is very unstable and new atoms, heat, and radiation as a byproduct. The chain of reactions that occurs emits alpha, beta, and gamma rays in which higher levels of exposure is fatal to all living beings. They act as bullets to DNA. The way these rays behave can be explained by the distance they travel through lead. Alpha rays can bounce off a lead structure with greater width, beta rays penetrate the lead structure and stop in a little distance whereas gamma rays can go deeper into the structure. Therefore, these rays travel through all living things and damage their cells.
A person exposed to a higher amount of radiation gets radiation burns which are very fatal and dies within days. The pain is unbearable, and no medications are yet found. A smaller amount of radiation exposure may cause cancers and disable childbirths. In the power plant, fuel rods are built such that no radiation leaks out to the environment. Numerous checks are done to ensure no radiation leaks from the reactor core.
Chernobyl Nuclear power plant
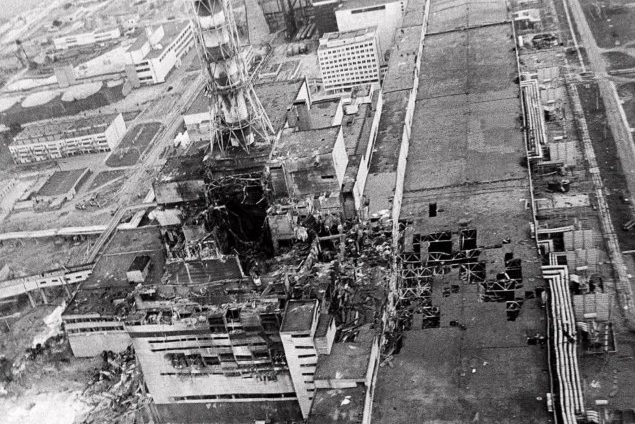
The Chernobyl power plant disaster is the most devastating nuclear accident in the history of the planet. It made about 2500 square kilometers of land on earth inhabitable for any living being for another 10,000 years. It is said that the radiation released was more than 100 times greater than the radiation produced from Hiroshima and Nagasaki bombs in world war II.
Chernobyl nuclear power plant was constructed between 1970 and 1977, is situated 16 km northwest of Pripyat, a city where the workers and their families of the power plant lived and 120km north of Kyiv, Ukraine. Chernobyl nuclear power plant had 4 RBMK-1000 design reactors that were capable to produce 1000 megawatts each. A core was about 7 m high and about 12 m in diameter. Ukraine was one of the Soviet Socialist Republics of the Soviet Union which was the world’s first Marxist-Communist state that became one of the largest and most powerful nations in the world between 1946 and 1991.
In 1986 April 26 at 1:23 am the Chernobyl power plant’s reactor number 4 blasted releasing tons of radiation to the open air. Around 30 workers who were at the plant and firefighters who approached the site to put up the fire died within 4 months of radiation poisoning. After 36 hours of the disaster, the closest city to the blasted site, Pripyat with about 50,000 residents were evacuated. Thereafter they evacuated around 300,000 people within 30 km radii from the power plant. The people in Russia, Ukraine, and Belarus were directly affected and present-day, this exclusion zone is within these countries.
The blast
It all started with the safety test. The objective of the safety test was to find out how long the dying turbines will spin to give enough power to the pump to regulate the water through the reactor, in a loss of main electrical power failure before the emergency generators power up. The test was conducted by the night shift operators who were less experienced in conducting this test.
At 1:23 am April 26th, 1986 the test begins. But the power raised uncontrollably, and an operator pressed the emergency shut down button which lowered all the control rods. In a normal nuclear reactor when the controlled rods are lowered the reactivity should be decreased. But during the test, a chain reaction inside the core was initiated which increased the reaction rate more. The power regulating system and emergency safety system and the emergency core cooling system were shut down to conduct the test. The excessive heat made the remaining water inside the core to evaporate and produced high pressure inside the chamber.
It is said that the head of the reactor number 4 section had seen the channels of the nuclear structure, which were 2000 tons in weight each, were moving up and down before the explosion. The power produced increased rapidly, and the core went out of control and exploded with the massive 1000-ton concrete roof.
The cleanup after the disaster
The firefighters from Pripyat who were not informed about radiation immediately arrives at the site without any protective gear and started distinguishing the fire. The Engineers were unable to decide what had happened and failed to find the reason. This kind of disaster was impossible, as they believed at that time and it took them hours to figure out that the reactor core has exploded and it was impossible to go near it. By morning, operators had shut down reactor No.3, No.1, and No.2. The radiation carried by wind was even detected in neighboring countries. It is said that some workers have put a lot of effort to minimize the damage done without considering they were exposed to radiation and many of them died afterward due to radiation.
Tons of sand, clay, Boron, and Lead were dropped from helicopters onto the burning reactor core to minimize the radiation release. The scientists figured out that there can be another explosion due to the meltdown of the remaining fuel and the thermal pressure built by it. To avoid this, three plant workers went inside the highly radiated building to open the valves of tanks to drain all the water trapped inside to avoid the production of steam which could cause the increase of pressure.
To prevent the contamination of the groundwater a tunnel was built without any machinery by some miners. They worked on the clock and saved miles of land from being contaminating. Hundreds of thousands of people who were firefighters, engineers, military troops, police, miners, cleaners, and medical personal were put to the cleanup process in which contaminated villages, farmlands were bulldozed, radioactive places were detected and soil which showed higher radioactivity was scraped off and buried.
The most challenging part was to clean the roof of the power plant to prevent any radiation release from scattered carbon chunks that were blown from the reactor. They sent robots to clean up, but they all stopped functioning because of higher radiation. Some other methods were also used, but those did not work well. So, soldiers had to approach the roof to clean up the carbon chunks and they were instructed to work there only for a few seconds to avoid exposure to a high dose of radiation.
After-effects of the disaster.
The exact death toll with premature cancer deaths hasn’t been calculated accurately. A drastic increase in thyroid cancer in children and children with birth defects were reported. Even today, the greatest number of cancer patients in Ukraine were reported closer to this area. This contaminated millions of acres of farmland in the region of Belarus, Russia, Ukraine, and parts of eastern Europe. A part of the forest in Chernobyl is now called the Red forest as different colored pine trees have grown.
Most radioactive ashes had landed or had passed this forest area on that day as the wind blew in that direction. So, this part of the forest is highly contaminated with radiation. Most areas within 30 km radii of the Chernobyl power plant are still radioactive. The cost of the disaster is huge and not yet calculated accurately and the after-effects of this disaster will continue for another 10,000 years or more.
To prevent radiation emitting from the reactor, workers made a concrete structure, the so-called sarcophagus (the Shelter), and encased the reactor in 1986. In 2016, it was enclosed in a large metal structure which is the largest movable structure in the world. It was 110m tall and 260m wide and expected to last for 100 years. The other 3 reactors are taken care of, even though they are shut down to prevent any further destruction.
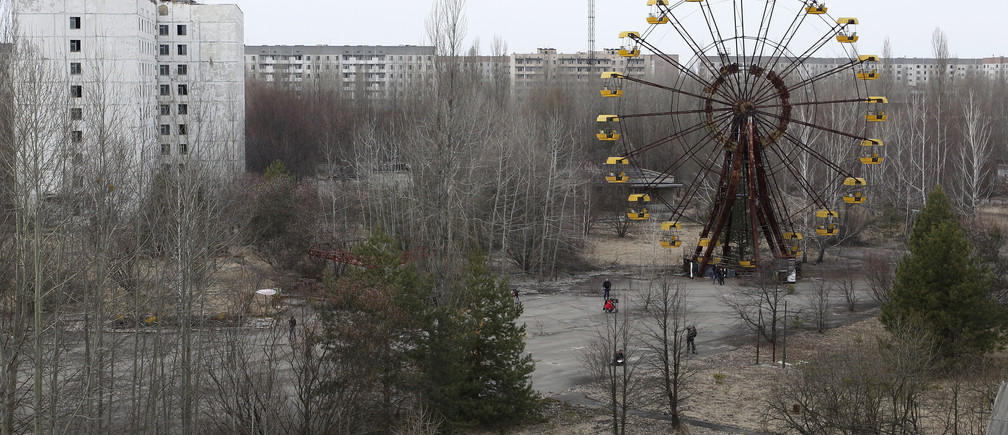
Today we can visit Chernobyl but avoiding the high radioactive areas. Thousands of tourists visit Chernobyl each year. You can still see abandoned houses, apartments, schools, administration buildings, and playgrounds. Pripyat is called a ghost town. Officially the 30 km radius area is an unhabitable area but about 100 villagers had come back again after the evacuation and they live there unofficially.
Lessons from history
There are different facts and myths about the way this disaster happened, but the true story and the scientific reasons for the blast were not revealed. The facts on the story are hard to find and most are hidden by the leaders at that time to prevent panic. There were many political changes due to this unexpected disaster. Numerous researches, articles, books, websites, videos, and TV series were produced related to the Chernobyl disaster. There are many tragic stories related to Chernobyl. It was a huge human error. But whatever the people say now, this disaster happened, and the victims still suffer.
At the beginning of this April (2020) a wildfire was broken inside the Chernobyl exclusion zone and according to news high radiation was detected at Kyiv, the capital city of Ukraine. The residents were advised to stay inside the houses to avoid exposure to rising radiation levels. As a result of this fire, the air quality in Kyiv is among the worst in the world. It was extinguished by firefighters and rain, but the radiation levels are still higher.
We cannot change the past, but we can prevent such disasters from happening again. Every person who works does a service to another human being. This disaster shows how much a human could affect the life of the planet. As a person who works, one must be responsible and aware of the work performed. This disaster could have been prevented if they had followed all safety precautions correctly. One small decision might have changed everything.
The recent nuclear disaster was the Fukushima nuclear power plant, Japan, in 2011 because of the earthquake and the tsunami caused as a result of the earthquake. Around 100,000 residents within a 3 km radius, were evacuated in the beginning, and then it was expanded to a 20 km radius.
Today there are 440 nuclear reactors in the world contributing to 10% of the electricity need of the world and more have been planned. France, the USA, UK, Spain, Romania, and Russia are the top countries that use nuclear energy to produce more than ¼th of its electricity needs. There are no nuclear power plants in Sri Lanka. But the closest nuclear power plant to Sri Lanka is in India where 22 nuclear reactors are working in seven sites inside India. Today the reactors are developed, and more safety precautions are taken so that no such nuclear disaster will ever happen. But no one can guarantee. Anyway, the countries which use nuclear power plants ensure the best has been done to provide safe power.
To 26th April 2020, 34 years have passed since the Chernobyl disaster. The people in Ukraine annually organize various events in schools to retrospect this disaster. During the week of 22nd to 26th of April, people who were there at that time, share their experience with young students. They remember all the workers in the powerplant who knew about the risks but stayed to control the situation, firefighters who died in radiation poisoning, miners, military and all other people who came to the site taking the risk and worked to prevent other explosions and to clean up the radiation. Eastern Europe and Russia are still livable thanks to these peoples’ dedication, sacrifice, courage, and bravery. We should all pay gratitude for them for minimizing the poisoning of our mother earth.
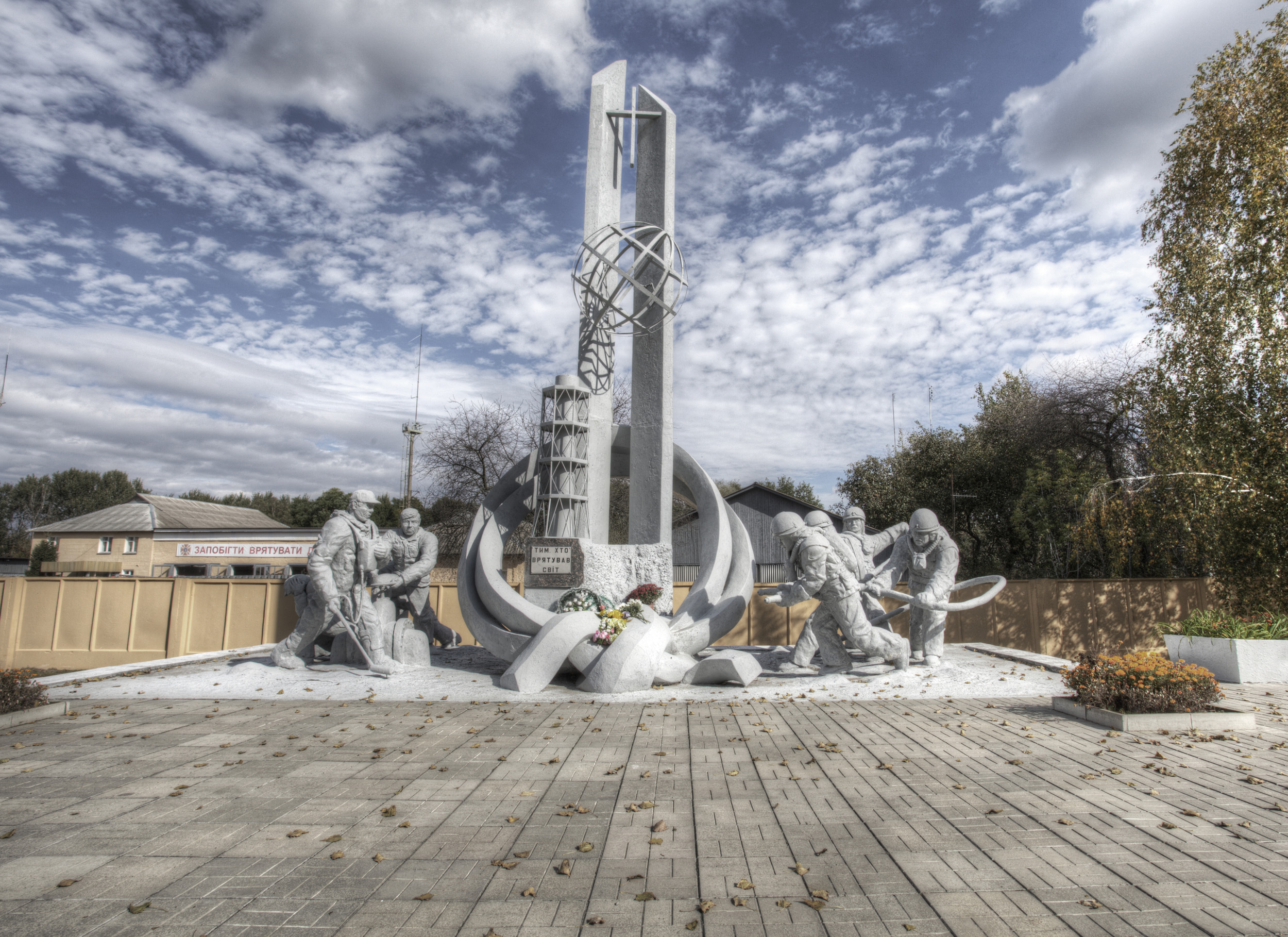
The memorial built ‘To those who saved the world’ in tribute to the firefighters and all other people who sacrificed their lives to overcome this catastrophe.
References
- https://nuclear-energy.net/
- https://bbc.in/3bB9mvH
- https://bit.ly/3cGLbw2
- https://bit.ly/2VxftLR
- https://bit.ly/2YcTImD
- https://bit.ly/3aDe36N
- https://bit.ly/2yAjIxj
- https://on.natgeo.com/3cGtMna
- https://bit.ly/2x7BXKc
- https://wordpandit.com/list-nuclear-powerplants-india/
- https://bit.ly/2S4rq9U
- https://www.history.com/topics/russia/history-of-the-soviet-union
- https://bit.ly/3bCC27M
- https://go.nasa.gov/355tPGK
- https://www.britannica.com/place/Soviet-Union
image courtesy
Featured image: https://bit.ly/3bFyGRu
- https://bit.ly/2KxcBbQ
- https://bit.ly/2VvK5xk
- https://bit.ly/3bCGKlG
- https://bit.ly/2Vzps3C
- https://bit.ly/3cJYjAq
- https://bit.ly/3atNXmQ
- https://bit.ly/3aC0ch8
- https://bit.ly/2Kvpgfb
- https://bit.ly/3bzPo4B
- https://bit.ly/3eMCv9d