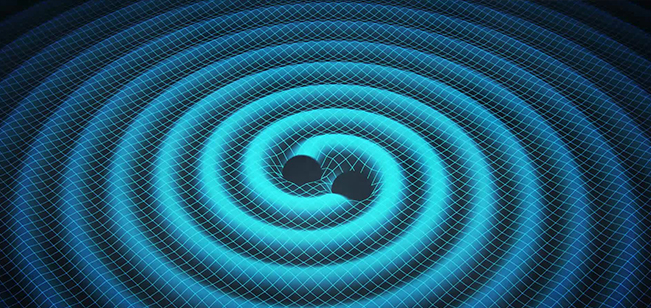
A team of physicists announced the discovery of gravitational waves on 11th February 2016 nearly a century after the first prediction done by Albert Einstein. These gravitational waves were theoretically predicted along with the general theory of Relativity in 1915.
These waves were detected on 14th September 2015 by both Laser Interferometer Gravitational Wave observatories (LIGO) located in Livingston, Louisiana and Hanaford, Washington, USA.
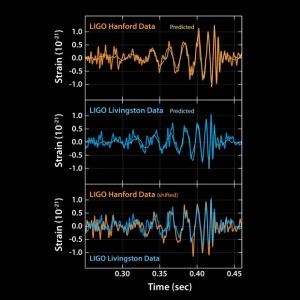
Why is this discovery so important for physicists?
According to the general theory of relativity, a pair of black holes which is orbiting each other would lose energy in the form of gravitational waves. This will in turn reduce the distance between them over billions of years. The two black holes will collide with each other forming a larger black hole. A fraction of the mass of this black hole will be converted into energy in the form of gravitational energy according to the famous equation .Such waves will travel through the universe in the speed of light.
The existence of these gravitational waves was initially demonstrated in 1974 by Joseph Taylor and Russell Hulse with the discovery of a binary system composed of a pulsar in orbit around a neutron star. The orbit was later found to be decreasing due to the generation of Gravitational waves. Later in 1993 The Nobel prize was awarded to them for this discovery.
Although gravitational waves had been detected before, the LIGO discovery was considered as the first direct observation which was done by measuring the tiny disturbances the waves made to space and time as they passed through the Earth.
What is LIGO (Laser Interferometer Gravitational Wave observatory)?

LIGO mainly consists of two widely separated 4 Km long interferometers. This is operated by scientists at the California Institute of Technology and the MIT. LIGO uses lasers to detect the differences in the length of the two perpendicular arms caused by the ripples in space-time which are also known as gravitational waves.
The original gravitational wave detectors of LIGO were completed in 1999. However, LIGO had been in operation since 2002, though LIGO was unable to detect any gravitational waves until 2010.As a result of the research that was done during this initial operation ,the LIGOs sensitivity was increased by a factor of 10 which led to an increase in volume, of the observable universe by 1000 times. These improvements also made it possible to measure a change in the lengths of the arms smaller than one-ten-thousandth the diameter of a proton (10-19 m). This advanced LIGO was first used for observations in September 2015.
References
https://goo.gl/5vI2iD
http://goo.gl/1NrCKl