Diabetes Mellitus (DM) or commonly known Diabetes is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by hyperglycemia resulting from defects in insulin secretion, insulin action or both. In simpler terms, it is a disease or a condition that occurs when concentration of a person’s blood glucose, also called blood sugar, is too high.
Blood glucose is the main source of energy for metabolism in a body. The blood vessels and blood are the highways that transport sugar from where it is either taken in or manufactured to the cells where it is used or stored. Sugar cannot go into the cells by itself. To solve this problem, the body produces insulin, a hormone secreted by the beta cells of pancreas. The pancreas releases insulin into the blood, which serves as the helper, or the “key,” that get into cells.
When sugar leaves the bloodstream and enters the cells, the blood sugar level reduces. Without insulin, or the “key,” sugar cannot get into cells. This causes blood sugar level to rise. Too much sugar in the blood is called “hyperglycemia” (high blood sugar).
Hence Insulin is an essential component in glucose homeostasis. Sometimes body doesn’t make enough—or any—insulin or doesn’t use insulin efficiently enough. Glucose then stays within blood and doesn’t reach cells as required.
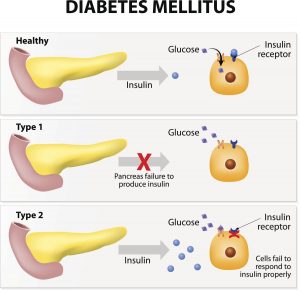
Types of diabetes
There are 2 main types of Diabetes as, Type 1 and Type 2. Type 2 is the cause for Diabetes Mellitus in 90% diabetic patients.
Type 1 DM, is a condition in which the pancreas produces little or no insulin due to destruction of the insulin-producing pancreatic cells by the body’s immune system.
In type 2 DM, the pancreas either produces inadequate amounts of insulin, or the body is unable to use the available insulin properly. The latter condition is known as insulin resistance. Type 2 usually occurs in adults, and is more common in people who are obese.
There are some additional factors that increase the risk of getting Diabetes. Some of them are: genetic factors, extra weight, bad communication between cells where cells send the wrong signals or don’t pick up messages correctly and broken beta cells where they send out the wrong amount of insulin at the wrong time.
Identifying Diabetes
Following are some main tests for diagnosing diabetes;
- RPG (Random Plasma Glucose): This is a blood test done at any time of the day to check the blood sugar level at that point in time selected randomly. If the RPG value is ≥200 mg/ dL (11.1 mmol/L) of blood, it indicates that the person has diabetes. Further tests may be required for confirmation.
- FPG (Fasting Plasma Glucose): This tests the amount of sugar in the blood stream after one has not eaten for 8–10 hours (overnight fasting). An FPG value ≥126 mg/dL (≥7.0 mmol/L) indicates that the person has diabetes.
- Glycated haemoglobin (HbA1C): This test measures how well the blood sugar has been controlled over period of time of the past 3 months. If the HbA1C is ≥6.5% (47.0 mmol/ mol), it indicates the presence of diabetes.
Prediabetes
Prediabetes is a condition in which the blood glucose levels are higher than normal level but not high enough for a diagnosis of diabetes. Millions of people worldwide do not know that they have prediabetes. That is why it is important to get screened for prediabetes. Prediabetic persons might develop type 2 DM in later life.
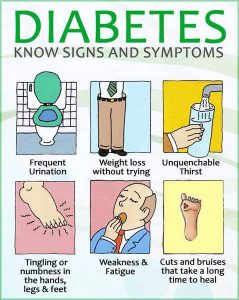
Symptoms of Diabetes
One of the most important things to remember is that diabetes does not always produce symptoms until the disorder reach fairly advanced state. If one has few of the following symptoms, one may suspect diabetes.
- Diabetes can affect the eyes. High blood sugar levels can cause the lens to swell, and the vision may become blurred or foggy.
- Become easily tired for no apparent reason.
- Pass urine more frequently than before.
- Hunger may increase and the person may eat more than usual.
- There may be weight loss despite a good appetite.
- A person may become overly thirsty and tend to drink excessive amounts of water. This is because the body tries to compensate for the water lost through the urine.
- A high blood sugar level makes it hard for the body to fight infections. Wounds do not heal easily, there may be frequent infections of the skin, bladder or gums, and itching in the genital area.
- There may be numbness or tingling in the hands and feet.
Treatments for Diabetes
The aim of treatment is to maintain the blood sugar level as close to normal as possible. There are various medicines to treat diabetes. Medicines for diabetes should be prescribed only by a health-care provider. Usually oral medication is the initial prescription. In severe conditions Insulin is administered. Insulin is currently not available in pill form, and hence it must be injected.
Complications of Diabetes
The complications of diabetes develop gradually. When too much sugar stays in the blood stream for a long time, it can affect the blood vessels, nerves, eyes, kidneys and cardiovascular system. Complications include heart attack and stroke, severe foot infections (leading to gangrene, which may result in amputation), end-stage kidney failure, sexual dysfunction and hypoglycemia which is reduction of blood sugar level than normal value.
Following important things help to prevent complications of diabetes:
- Take medicines regularly as prescribed by the health-care provider.
- Keep a track of the blood sugar level by going for regular tests and check-ups.
- Eat healthy – more vegetables and fruit, less fatty, sugary and salty food.
- Stay physically active.
- Be alert for skin infections and skin disorders.
- Go for regular check-ups.
- Watch for any tingling, burning, loss of sensation, and wounds on feet.

Prevention of Diabetes
Diabetes is a disease condition that usually is possible to avoid or control with minimum efforts, if not affected by genetic factors or serious physiological malfunctions. Practicing a healthy lifestyle as mentioned above helps achieving this. Regular checkups and good attention on personal health makes it easier.
In addition, communities and civil societies can create awareness about diabetes, its complications and prevention. Advocating people for physical activity and healthy diets in educational institutions and workplaces also helps.
Diabetes can cause serious health problems such as heart disease, stroke, blindness, kidney failure, among others. If not controlled it can easily cause the death of a person. Hence it is a silent killer. Thus diabetes should not be treated with negligence or taken lightly. Unfortunately diabetes has no permanent cure discovered yet. However it is possible to take steps to manage diabetes, keep blood glucose level in check and stay healthy.
References :
- https://www.webmd.com/diabetes/type-2-diabetes#1
- https://www.idf.org/aboutdiabetes/what-is-diabetes
- https://www.medicinenet.com/foot_problems_diabetes/article.htm
Image Courtesy :
- Title image : https://bit.ly/2Mtms2O
- 1st content image : http://shorturl.at/mwOR2
- 2nd content image : http://shorturl.at/gqEIL
- 3rd content image : http://shorturl.at/bhnH1
- 4th content image : http://shorturl.at/bHJNP